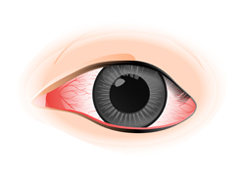
Redness in the conjunctiva
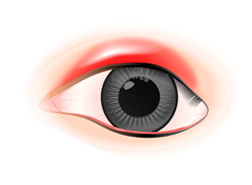
Red and droopy eyelids
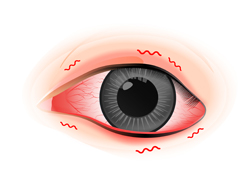
Itchy and painful eyes
Feeling something in the eyes,
burning sensation
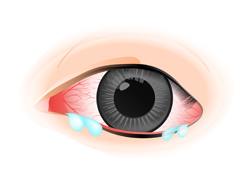
Tearing and sensitive to light
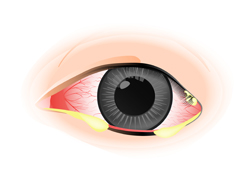
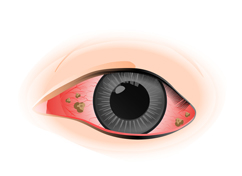
Thick discharge
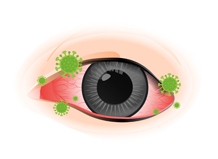
It is usually related to upper respiratory tract infection and caused by viruses. The main pathogens are adenovirus and enterovirus. This type of conjunctivitis is highly contagious, but the infected eye(s) usually recovers without treatment within a few days.
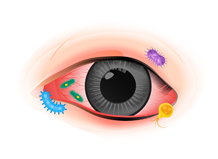
It is caused by a variety of bacteria, the most common are Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Both new-born babies and adults can be infected by Chlamydia. If bacterial conjunctivitis is not treated, the bacteria can cause serious damage to the eyes.
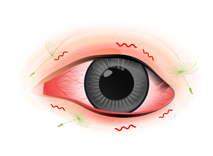
Allergic conjunctivitis is a common eye disease. When the allergens lead to inflamed eyes, microorganisms and environmental irritants, the immune system will overreact in responding to the allergens, causing the swollen blood vessels walls in conjunctiva and therefore the eyes become pink or red.
The following are common types of allergic conjunctivitis:
It usually occurs in spring and summer. The common allergens are mold spores, and plant pollen in the alternation of spring and summer. People with allergies, such as: asthma, allergic rhinitis, are more likely to suffer from seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
Allergens mainly are air pollutants, dust, dust mites or animal dander, etc. Allergic symptoms may occur in the whole year; however, the symptoms are mostly mild.
Giant papillary conjunctivitis (GPC) is the most common complication of long-term use of contact lenses. A long-term wearing of contact lenses can cause roughness of the conjunctiva, so if contact lenses are not properly selected, examined, worn, or cared for, complications and sequelae will occur.
Conjunctivitis can be divided into infectious and non-infectious causes. Viral and bacterial are extremely infectious, can be infected by close contact with the patient or indirect contact with contaminated items.
Common ways of transmission:

Touching the infected individuals’eyes or upper respiratory tract secretions with hands.

Sharing personal items, such as: towels, clothing, eye cosmetics or eye drops.

If swimmers swim in a contaminated pool, they could also be infected.
 The incubation period is usually 1-12 days after exposure for bacterial conjunctivitis. It takes about 10 days to several weeks from the onset of symptoms until recovery.
The incubation period is usually 1-12 days after exposure for bacterial conjunctivitis. It takes about 10 days to several weeks from the onset of symptoms until recovery.
Conjunctivitis can occur at all ages, but those below are most frequently affected.
Children under 5
People who have sensitive eyes and noses
People who have
vulnerable immune system
People who always touch their eyes
People who wear contact lenses for a long time
People who stare at screens forS a long time
Normally, viral conjunctivitis heals within 1 week without treatment. Patients can take more rest and apply cold wet towels on the eyes (several times a day, with eye closed) to relieve the symptoms of discomfort.
The bacterial conjunctivitis is usually treated with medications that to be prescribed by doctors, such as eye drops or ointments containing antibiotics.
If the conjunctivitis is caused by the allergens, avoiding contact with allergens can reduce symptoms or prevent relapse. Contact lenses should be stopped if they cause conjunctivitis. Clinically, the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis can also be relieved by medications.
Don’t share personal items like towels, pillows, eye droppers, eye cosmetics, contact lenses, or other items that may touch your eyes.
Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before touching your eyes and always maintain good hygiene.
Avoid using the public facilities such as swimming pool, public bathroom, sauna, and playground while in the outbreak of conjunctivitis.
Clean both sides of your contacts with fresh contact lens disinfecting solution, rinse and leave them to soak overnight (at least 6 hours).
Be aware of allergens such as pollens, house dust mite, and animal dander etc, especially when season changed.
